What’s the Difference Between JPG and PNG Formats? After Reading This, Don’t Choose the Wrong One Again.

In image processing, we commonly encounter two image formats: JPG and PNG. Many people don't understand the differences between these two formats, but choosing the wrong one can result in low-quality images or unnecessarily large file sizes. Understanding the distinctions between these formats will help you avoid such issues.
Today, we'll introduce these two image formats to help you make informed choices when using them.
What is the JPG File Format?
Advantages: Small file size, adjustable compression level, supported by all browsers and editors
Disadvantages: No transparency support, lossy compression reduces quality
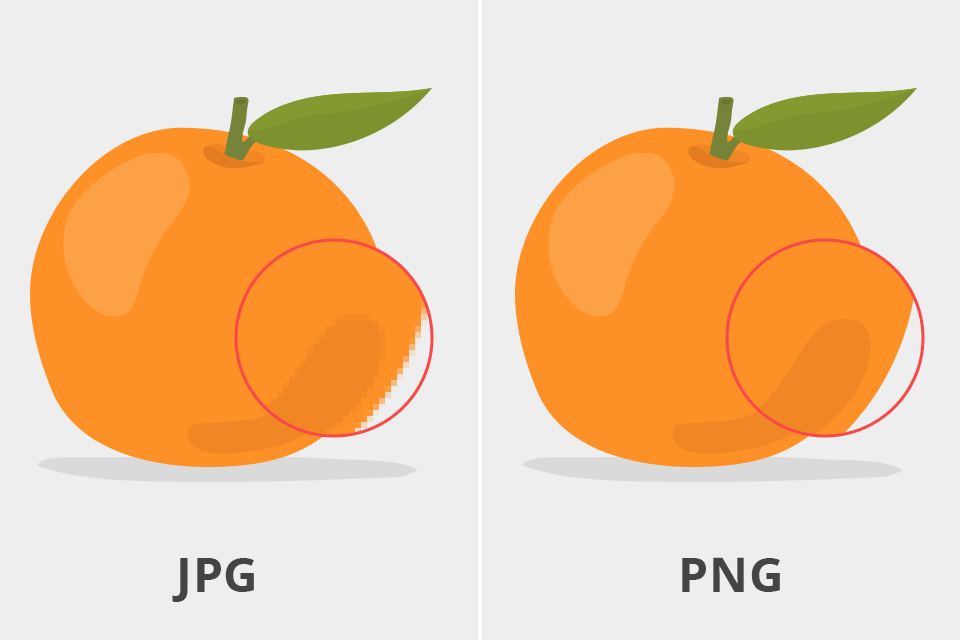
The JPG format has become the standard compression format for digital photography and online image sharing because it strikes a good balance between file size and image quality. Cameras and websites typically use this format. JPG files are smaller, making web pages load faster. However, when photographers need professional-quality photos, JPG files can become quite large. Additionally, JPG uses lossy compression, meaning image quality is compromised to minimize file size.
What is the PNG File Format?
Advantages: Lossless compression, supports transparency
Disadvantages: Larger file size
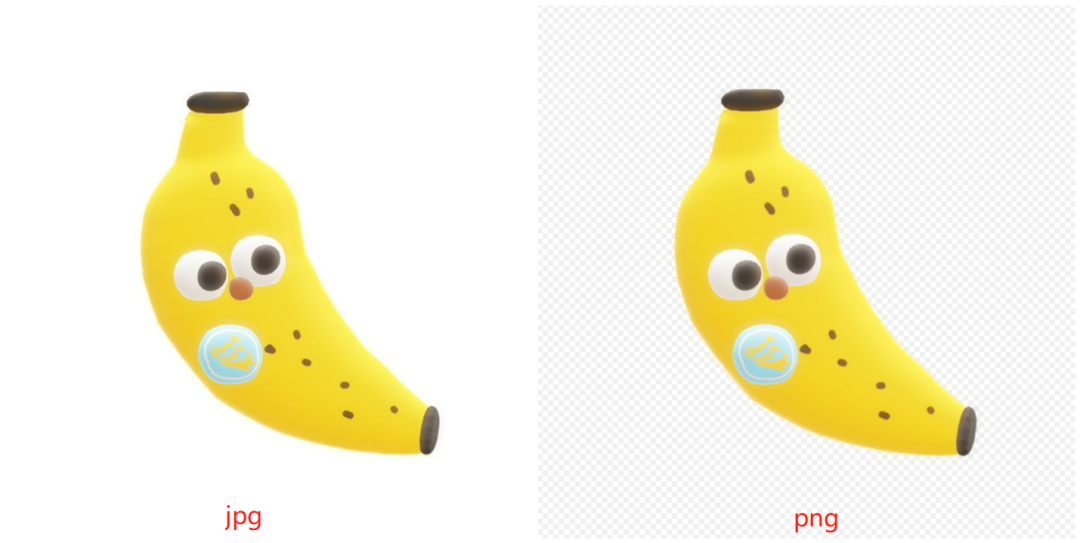
PNG saves files without quality loss, making it ideal for web images with transparent backgrounds, logos, charts, and illustrations. However, it's not the best choice for storing photos due to its larger file size. A key advantage of PNG is its transparency support, applicable to both color and black-and-white images. Often, a checkerboard background is used to indicate transparency. PNG is not suitable for storing large quantities of high-quality files, as it consumes significant storage space. It's also not ideal for images intended for printing, as it doesn't support non-RGB color spaces like CMYK.
What's the Difference Between JPG and PNG?
1. Compression Level
When choosing between these file formats, designers typically consider their compression types. Lossless compression reduces file size without quality loss, allowing you to shrink files while maintaining original quality. This format category is widely used for illustrations, text materials, or drawings. Lossy compression, on the other hand, sacrifices some data during compression, making it impossible to restore the original quality. When saving files in JPG format, quality is reduced, which is why many photographers prefer saving images in uncompressed formats. Uncompressed formats occupy the most disk space but provide the most accurate image representation.
2. File Size

Although JPG files have lower image quality, they occupy less hard drive space, making them particularly useful for those with limited storage. Such images also load faster. The most significant difference between JPG and PNG files is that the latter contains more information, resulting in larger sizes and higher quality. This is why PNG images take longer to load on web pages compared to JPG.
3. Transparency
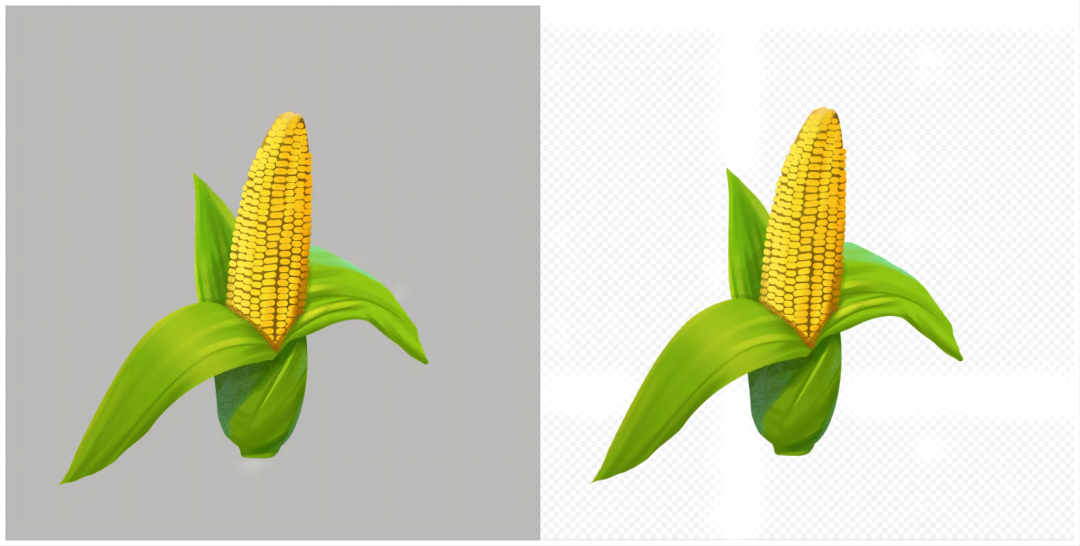

PNG excels in transparency support, while JPG doesn't support transparency at all. When photographers use Photoshop to separate an object from its background, PNG format already has an empty background, eliminating the need for additional editing. PNG images with transparent backgrounds can be used directly.
4. Color Mode Compatibility
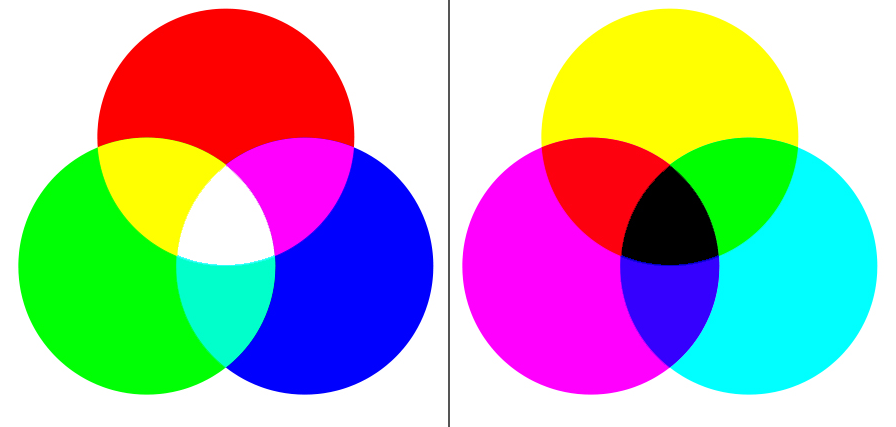
RGB is used for displaying color images on screens, while the CMYK system was created for printing. PNG format doesn't support CMYK mode, making it unsuitable for files intended for printing.